ABSTRACT
The use of Natural medicinal plant to manage HIV/AIDS has recently gained public interest, many research have been done on the ethnomedicine around the globe. Although there have been no medicine licensed till date, this policy remain an arguable issue in many countries. Plants and other natural products present a large repertoire from which to isolate novel anti-HIV active compounds. In this research work, with HOOIMM PLUS (A, B, C, D, E), an anti viral herb-drug manufactured by HOOTONE REMEDIES, have a composition of 33 different plant species those are found in India, were found to contain anti-HIV active compounds that included diterpenes, triterpenes, biflavonoids, coumarins, gallotannins, galloylquinic acids, curcumins and limonoids etc. They also contain the high phenolic content and the presence of polar substances, such as flavonoids and tannins which are known to possess antiviral activity. These active compounds inhibited various steps in the HIV life cycle. The main objective of this study was to carry out a database survey of literature for plants and their natural products with anti-HIV active compound present in HOOIMM plus. Such a Bioinformatic database survey is an important prerequisite and starting point in the search for novel HIV/AIDS treatments from natural plants.
INTRODUCTION
Natural products remain a prolific source for the discovery of new drugs. The recent data suggests that 80% drug molecules are natural products or natural compound. Studies on source of new drugs from 1981 to 2014 reveal almost half of the drugs approved since 1994 are based on natural products. Indian natural products have contributed towards this “boom” in drug discovery. The drug discovery process from plant is, however a laborious and time consuming process. This research article focuses on the laborious and time consuming process. This research article focuses on the role of natural medicinal plants to manage HIV/AIDS and the related opportunistic infection.
The conventional rediscovery process aims to identify a single, pure active constituent from an active extract and a method to estimate it in the crude drug. The classical example of drug discovery like morphine, quinine, digoxin, etc which replaced the extracts of their respective plants were mostly responsible for harbouring the idea that a single active ingredient must have been responsible for the bioactivity. The drawback of this ideology is that it does not look into the synergy or antagonism characteristics present in the mixture. Apart from this some constituents may also possess other diverse activities. This factor is confirmed by several examples reported in literature where the ascribed pharmacological activity of the extracts could not be matched with that of the isolated pure compounds. Most of the newer work on medicinal plants is mostly the rediscovery of effects known for a long period of time at cellular and molecular levels. The uncertainty of earlier studies is obvious in case of biological activity because of the lack of standardization technique or instance where even if present were in a primitive state.
The natural plant medicine has a very long term history of usage in a number of disease and disorders, however, the main constituent mainstay and the mechanism of action being unclear. But recently, it has been suggested that drug discovery should not always be limited to discovery of a single molecule and the current belief “one disease-one drug” approach may be untenable in the future and that rationally designed polyherbal formulation could also be investigated as an alternative in multi-target therapeutics and prophylaxis. Development of standardized, safe and effective herbal formulations with proven scientific evidence can also provide an economical alternative in several disease areas. Still some pro’s and con’s need attention for improvement of natural medicines.
HIV/AIDS-related diseases remain one of the leading causes of death globally. According to UNAIDS, the number of people living with HIV/AIDS worldwide was estimated at 35 million. The current antiretroviral drugs have many disadvantages including resistance, toxicity, limited availability, high cost and lack of any curative effect (Vermani and Garg, 2002). These shortcomings of conventional ART continue to open new vistas in the use of ethnomedicinal plants and other natural products for the management of HIV/AIDS.
In many countries, the inclusion of anti-HIV ethnomedicines and other natural products in official HIV/AIDS policy is an extremely sensitive and contentious issue. It is sensitive because anti-HIV ethnomedicines and other natural products can easily become a scapegoat for denial and inertia to roll-out ART. It is also contentious because in various resource-poor settings, government-sponsored ART programmes discourage the use of traditional medicines, fearing that the efficacy of antiretroviral drugs may be inhibited by such natural products, or that their pharmacological interactions could lead to toxicity. Reliance on anti-HIV plants and other natural products can also lead to poor adherence to ART (Langlois-Klassen et al., 2007). Thus, many governments still have contradictory attitudes towards the use of anti-HIV plants and other natural products in the management of HIV/AIDS, discouraging them within ART programmes, and supporting them within other initiatives of public health and primary health care.
As early as 1989, the World Health Organization (WHO) had already voiced the need to evaluate ethnomedicines and other natural products for the management of HIV/AIDS: “In this context, there is need to evaluate those elements of traditional medicine, particularly medicinal plants and other natural products that might yield effective and affordable therapeutic agents. This will require a systematic approach”, stated a memorandum of the WHO (1989).
The objective of this study was to carry out a database survey of literature for plants and other natural products with anti-HIV active compound present in HOOIMM PLUS.
a Bioinformatic database survey is an important prerequisite and starting point in the search for novel HIV/AIDS treatments in natural plants. However, further studies are needed to determine their interactions with current regimes of antiretroviral drugs. More clinical trials of candidate drugs developed from these novel compounds are also encouraged.
METHODOLOGY
The different plant species with their active HIV compound were searched in PubMed Central, the United States of America National Library of Medicine’s digital archive of biomedical and life sciences journal literature. During the literature search which lasted 3 months, between 300 journal publications were reviewed. Wherever possible, families and species of plants and other natural products, their active compounds and modes of action, were Evidence of use of plants and other natural products against HIV/AIDS was kept unrevealed to maintain the term and policy of pharmaceutical company (HOOTONE REMEDIES), so different codes were given for different active constituents.
Table 1.1: Showing Mechanism of action of various active constituents found in HOOIMM plus.
DISCUSSION
Several chemical compounds were found to interfere with HIV entry into cells while other were active against HIV reverse transcriptase, integrase, protease, and general replication. Most of the entry inhibitors stopped the spread of HIV among cells. Some of them binds to glycosylated viral envelopes blocked HIV-1 entry into cells. A compound isolated targeted gp120 proteins and blocked fusion of HIV-1 to lymphocyte. A crude drug inhibited HIV-1 gp120 binding to CD4 cells, inhibited the binding of gp120 to cells expressing CXCR5 receptors. Inhibited cell-to-cell transmission of HIV-1inhibited HIV-1 entry into lymphocytes. Three different chemical compounds were known to be active against HIV reverse transcriptase (Table 1). Three active compounds were observed to be HIV protease inhibitors. Two active compound were observed to be HIV integrase Inhibitor. Some active compounds were found to inhibit syncytia formation, a property of HIV that makes infected and healthy CD4 cells to fuse and form one giant cell. Many active compounds were known to inhibit general HIV replication. Some plant-derived compounds were reported to possess activities against HIV-related symptoms.
CONCLUSION
The literature survey revealed several anti-HIV active compounds such as terpenoids, coumarins, polyphenols, tannins, proteins, alkaloids, and biflavonoids that inhibit various steps of the HIV life cycle. These active compounds were isolated from 33 Plant species. Phylogenetic analysis and other bioinformatics tools may shed light on unidentified but related plants and other organisms that may contain similar active compounds. Primary data of known active compounds and mechanisms of action were available from studies. Pharmacological interactions of unknown active ingredients from herbal medications remain a source of great medical concern. Throughout the survey, it was clear that although several medicinal plants, most of the research on screening of plants and isolation of active compounds was carried out elsewhere in Asia, Europe and the Americas. in vitro tests against HIV, and mechanisms of action is highly needed. There is also an urgent need to fast-track HIV/AIDS clinical trials of candidate drugs developed from novel compounds isolated from plants and other natural sources. This will ensure that the millions of people that require HIV/AIDS treatment will have access to newer, more effective, and less toxic drugs.
REFERENCES
-
- Fletcher CV, Kakuda TN, Collier AC (2002). Bone and joint infections. In: JT Dipiro, RL Talbert, GC Yee, GR Matzke, BG Wells, LM Posey (eds) Pharmacotherapy- a pathophysiologic approach. Mcgraw-Hill Medical Publishing Division, United States of America, 5th edition, pp. 2151–2174.
-
- Gustafson KR, Sowder RC, Henderson LE, Cardellina JH, McMahon JB, Rajamani U, Pannell LK, Boyd MR (1997). Isolation, primary sequence determination, and disulfide bond structure of cyanovirin- N, an anti-HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) protein from the cyanobacterium Nostoc ellipsosporum. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 238: 223-228.Hardon A, Desclaux A, Egrot
-
- Langlois-Klassen D, Kipp W, Jhangri GS, Rubaale T (2007). Use of traditional herbal medicine by AIDS patients in Kabarole District, estern Uganda. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 77: 757-763. Vermani K, Garg S (2002). Herbal medicines for sexually transmitteddiseases and AIDS. J. Ethnopharmacol. 80: 49-66.
-
- Vermani K, Garg S (2002). Herbal medicines for sexually transmitted diseases and AIDS. J. Ethnopharmacol. 80: 49-66.
-
- World Health Organisation (WHO) (1989a). In vitro screening of traditional medicines for anti-HIV activity: memorandum from a WHO meeting. Bull. World Health organization 87: 613–618.
-
- World Health Organisation (WHO) (1989b). Report of a WHO Informal Consultation on Traditional Medicine and AIDS: In Vitro Screening for Anti-HIV Activity. Global Prog. AIDS and Trad. Med. Programme, pp. 1–17.
ABSTRACT
Quantification of human immunodeficiency virus type-1 (HIV-1) proviral DNA is increasingly used to measure the HIV-1 cellular reservoirs, a helpful marker to evaluate the efficacy of antiretroviral therapeutic regimens in HIV-1infected individuals. Furthermore, the proviral DNA load represents a specific marker for the early diagnosis of perinatal HIV-1 infection and might be predictive of HIV-1 disease progression independently of plasma HIV-1 RNA levels and CD4+ T-cell counts. The high degree of genetic variability of HIV-1 poses a serious challenge for the design of a universal quantitative assay capable of detecting all the genetic subtypes within the main (M) HIV-1 group with similar efficiency. Here, we developed a highly sensitive real-time PCR protocol that allows for the correct quantification of virtually all group-M HIV-1 strains with a higher degree of accuracy compared with other methods. The study involves the detection of HIV proviral DNA from blood sample of treated patients and their current status of Plasma RNA load and CD4+ count for correlation.
INTRODUCTION
Individuals infected with HIV-1 are generally followed by monitoring the plasma viral RNA loads and CD4+ cell counts, which are markers of viral replication and immune function, respectively (Mellors et al., 1996; Pantaleo et al., 1993). The plasma viral RNA level predicts minimally the rate of subsequent CD4+ cell decline (Rodríguez et al., 2006) and is used commonly as a marker of the outcome of highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART). Although the plasma viral RNA level in the majority of patients receiving HAART declines below the detection limit within a few months after the start of therapy (Gallant et al.,2006), proviral DNA is detected persistently in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) or lymphoid tissue (Chun et al., 1997; Sonza et al., 2001). Several studies have suggested that measuring the proviral DNA level may be important for evaluating the longterm effectiveness of HAART (Burgard et al., 2000; De Milito et al., 2003; Pellegrin et al., 2003), while this is sometimes conflicting (Soriano-Sarabia et al., 2007).
The HIV-1 proviral DNA load could be an alternative viral marker, as it is known that proviral DNA persists in infected cells, even after prolonged successful HAART as evidenced by undetectable plasma RNA viral load. A decline in DNA might indicate a long-term impact of the HAART on the reservoirs and the long-term effectiveness of the Support. But data regarding the decline in DNA are sometimes conflicting. Some authors noted decreased levels after one year of antiretroviral triple combination therapy and others reported stable HIV-1 DNA levels over several years in ART naive patients.
The quantification of HIV type 1 proviral DNA in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) have previously been reported, and many of them are based either on the principle of conventional PCR requiring post PCR analysis or on real-time PCR on total PBMC, using specific probe detection.
Real-Time PCR Method
Real-time PCR is becoming increasingly popular as a method for the quantitative detection of DNA and RNA viruses. Besides its research applications, an accurate determination of the viral load, whether cell associated or free in biological fluids, can provide critical information in the clinical setting for the diagnosis and staging of acute and chronic viral infections, as well as for guiding Support interventions and assessing their efficacy. In addition, real-time PCR has been applied for screening purposes to measure the level of contaminating viruses in blood donations or plasma pools for the production of blood derivatives.
HIV Diversity
The circulating strains of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) have been classified into 3 major phylogenetic groups, termed M, N, and O, all of which cause HIV/AIDS in infected individuals. GroupM (for “major”) comprises the great majority of HIV-1 infection worldwide and has been further subdivided into 12 distinct lineages, termed subtypes (AD, FH, and J), and circulating recombinant forms (AB, AE, AG, and AGI). Group O (for “outlier”) comprises many fewer isolates that are geographically restricted to west central Africa. Finally, group N (for “non-M/non-O”) was discovered recently and is the least widespread of all HIV-1 lineages. Viruses belonging to this group have thus far only been identified in a handful of individuals, all of whom were residents of Cameroon. Sequence variation among members of these various lineages is extensive, with nucleotide sequence variation in the env gene with a range of 18% among the different group M subtypes and circulating recombinant forms (CRFs) to nearly 42% among members of all 3 groups. Given this extent of diversity, it is not surprising that the great majority of nucleic acidbased diagnostic tests originally designed for group M, subtype B viruses have reduced sensitivities in detecting viruses from other groups and subtypes.
Methods
Assay design
Quantification of the HIV-1 proviral DNA is increasingly used in the clinical follow-up of HIV-1infected individuals. However, due to the high degree of genetic variability of HIV-1, the identification of a PCR amplicon that guarantees the same efficiency of amplification with all the genetic subtypes of the main (M) HIV-1 group represents a major challenge to the design of a universal assay. We have developed an HIV-1 group M-specific quantitative realtime PCR assay that measures the HIV-1 proviral DNA load with a similar degree of sensitivity and accuracy regardless of the viral genetic subtype. The success of this protocol for the quantification of HIV-1 proviral DNA relies on the optimized design of primers and probe, which ensures the correct quantification of virtually all circulating group-M HIV-1 strains. Moreover, this assay is so robust that it can quantify DNA derived from a crude lysate with the same degree of accuracy as with purified DNA. As a starting point, we selected a region spanning parts of the HIV-1 LTR, which is highly conserved among all circulating group-M HIV-1 subtypes. The selected region is completely conserved in about 96% of the HIV-1 sequences present in the NCBI database. A realtime PCR assay was developed by designing two specific primers, and a probe within the selected LTR region.
We evaluated the accuracy and sensitivity of the HIV-1 of different genetic subtypes, some of which were carrying mutations in either the primers or the probe sequences. The modified assay was able to accurately measure proviral DNA from all the primary HIV-1 isolates tested with similar efficiency regardless of genetic subtype as well as from clinical samples derived from HIV-1-infected patients. The assay involves quantification in PBMC of HIV-1 seropositive patients. As 95 to 99% of infected cells are CD4+ cells, we developed a relative quantification assay of HIV-1 proviral DNA in purified CD4+ cells. Here, we have developed a multiplex real-time PCR for quantification of HIV-1 LTR DNA and the CCR5 gene in CD4+ cells using TaqMan probes. Sequence-specific hybridisation probes provide the most specific real-time analysis of amplified target sequences.
Cd4+ cell isolation
CD4+ cells were isolated from 10 ml of patient EDTA whole blood samples by an immunomagnetic method using anti-CD4 coated magnetic beads (Dynabeads® CD4 Positive Isolation Kit) according to the manufacturer’s protocol and were stored at -80°C until use. The complete process takes approximately 3 hours and the purity of the CD4+ cell preparation was about 99% as estimated by Becton Dickinson Fascan Flow Cytometer technology.
DNA purification
DNA was extracted from purified patient CD4+ cells diluted in 200 µl PBS, using the Sigma Aldrich, GeneElute, (Cat. no. NA2020), according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Particular attention was paid on DNAse and RNAse free materials. Depending on the number of samples, the whole DNA purification process required approximately 1 hour.
HIV-1 DNA real time PCR assay
A series of dilutions of HIV-1 DNA standard corresponding to 106 to 100 was included in each experiment in order to generate an external standard curve. The PCR mixture (total volume 20 μl) in nuclease free water contained MyTaq™ HS DNA Polymerase, final concentrations of 3mM MgCl2 and 0.5μM of each primer and 5μl of purified DNA or negative control. All samples were analysed in duplicate. The amplification protocol for HIV-1 on the CFX96™ (IVD) BIORAD was as follows: a 5 min denaturation step at 95°C for polymerase activation, of 45 cycles consisting of 15 seconds at 92°C, 1 minute at 65°C. The fluorescence was measured at the end of each elongation step. A fragment from the CCR5 gene was amplified in parallel with the HIV-1 LTR gene to quantify the total number of investigated cellular purified DNA of CD4+ cells.
Sample collection
The study based on the selected patient those who have undergone Support with the Anti-HIV Support. Here, we have reported the status of Qualitative proviral DNA, Quantitative HIV-1 RNA RT-PCR, Western blot Assay, qualitative antibody assays for all the five treated HIV patients. Nevertheless, CD4 cells enumeration at present.
Technical resources for HIV-1 status.
- Identification of serostatus: HIV COMB approved by USFDA
- Detection of HIV-1/2 antibody and band profiles: Genelab HIV Blot 2.2 approved by USFDA
- HIV-1 (RT-PCR) Quantitative assay: Real time Cobas Taqman approved by USFDA
Results:
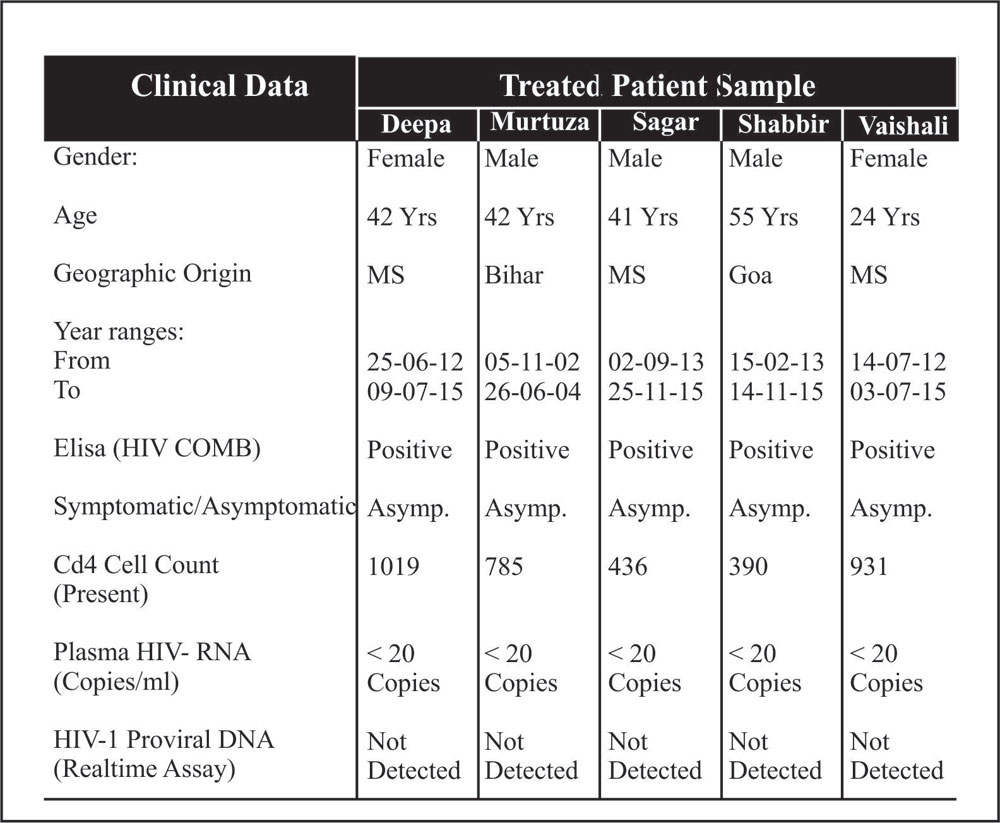
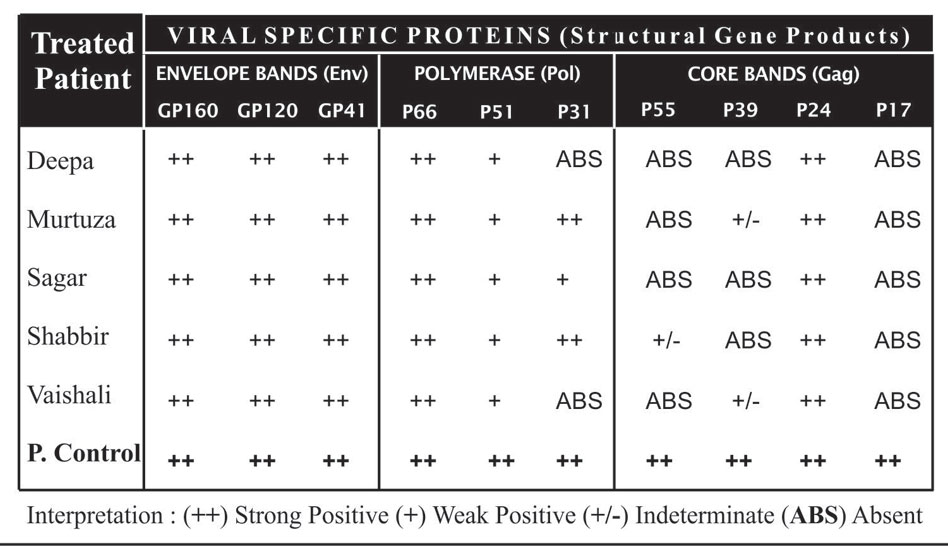
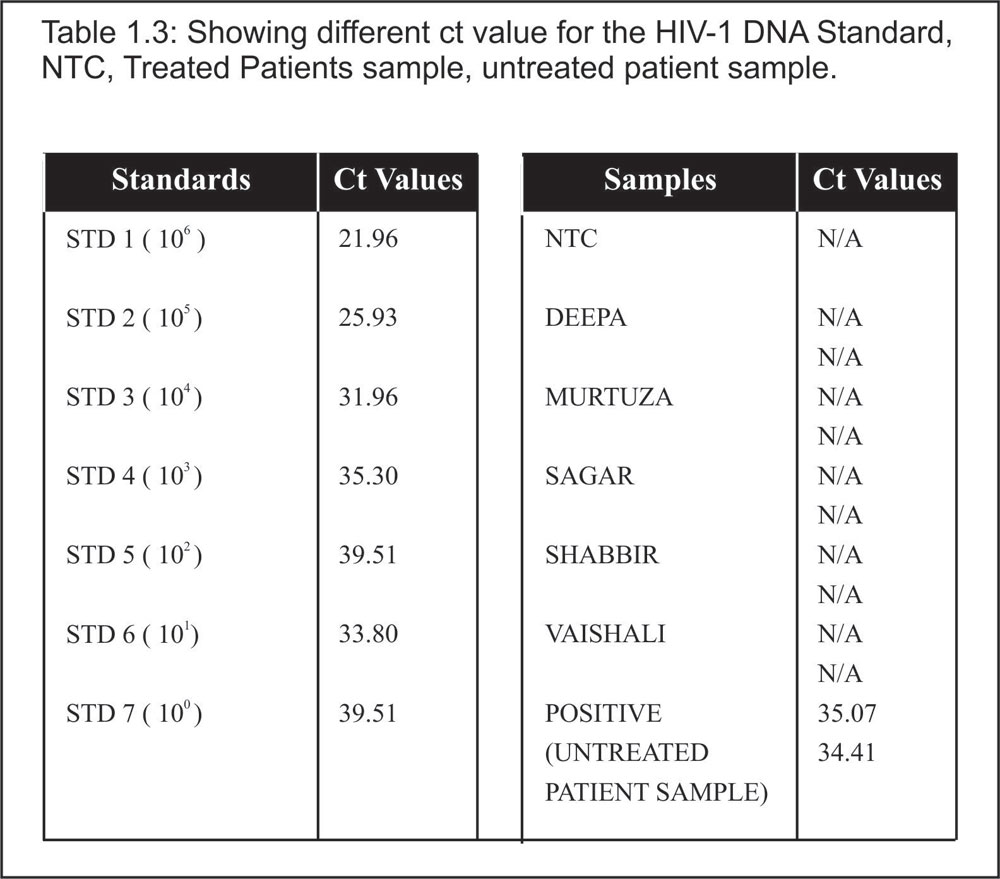
It has been found that after the Support, all the four patients were HIV asymptomatic seropositive, since their report showing positive with HIV COMB (Followed the Manufacture’s protocol) (Table 1.1). Plasma viral load were detectable for all treated patient. The table 1.2: show different western blot band profile in the serum (Detection Genelab HIV Blot 2.2 USFDA) confirming the HIV Antibodies and HIV type. The blood samples were reported HIV-1 type for all individual. Table 1.1, Figure1, 1.2 and Table 1.3: shows proviral DNA not detected for all five treated patient.
Table 1.1: Patient characteristics
Table.1.2: Showing western blot band profiling of the 5 treated patients.
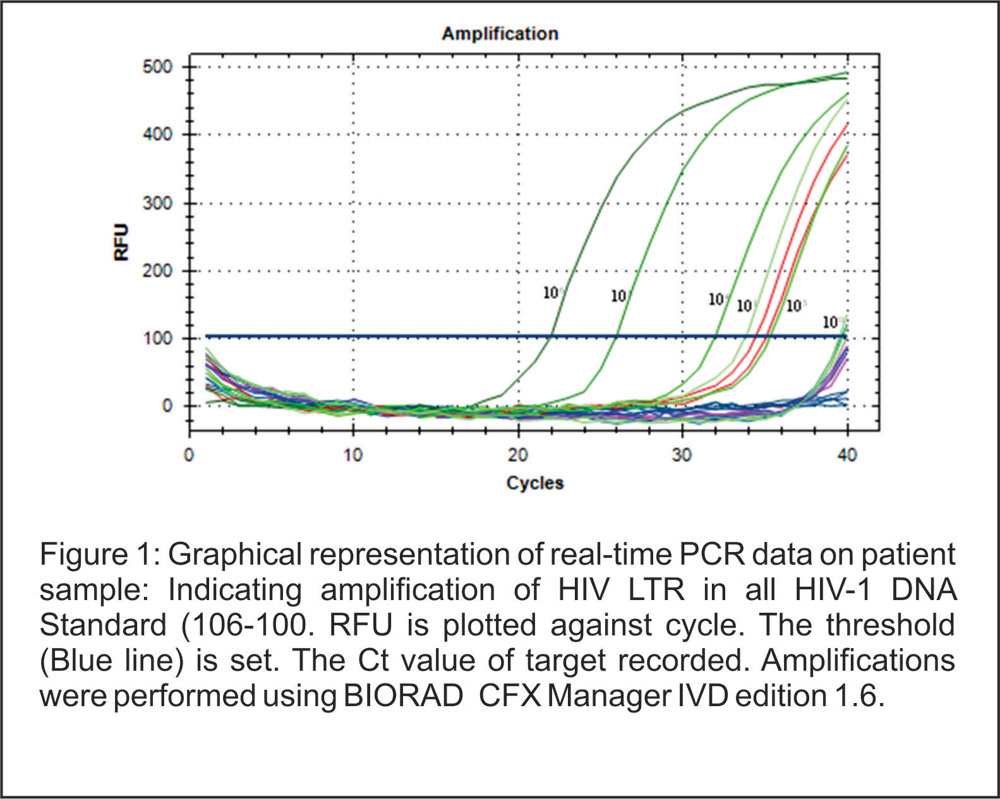
Figure 1:
Graphical representation of real-time PCR data on patient sample: Indicating amplification of HIV LTR in all HIV-1 DNA Standard (106-100. RFU is plotted against cycle. The threshold (Blue line) is set. The Ct value of target recorded. Amplifications were performed using BIORAD CFX Manager IVD edition 1.6.
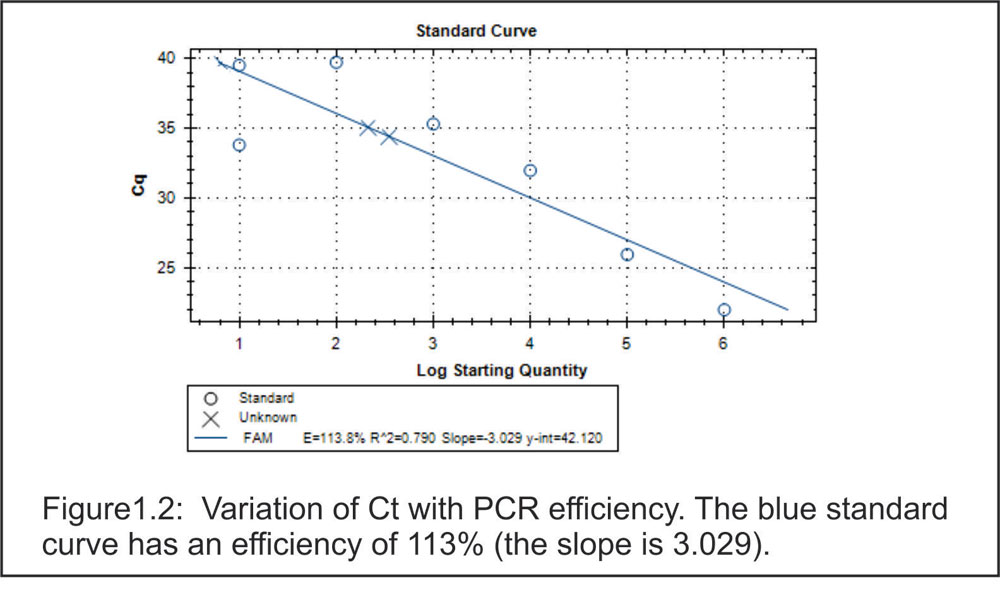
Figure1.2:
Variation of Ct with PCR efficiency. The blue standard curve has an efficiency of 113% (the slope is 3.029).
Table 1.3:
Showing different ct value for the HIV-1 DNA Standard, NTC, Treated Patients sample, untreated patient sample.
Invitro Lab Studies
In invitro lab studies, this drug was put for Drug Sensitivity Test and Anti-retroviral Activity Test in the laboratory adhering to the standard protocol and the highest inhibition rate of 98% was recorded against the causative agent, HIV virus. The detail procedures undertaken in an invitro lab study are mentioned as under: –
Methods :
1. Collect 20 ml Blood in an EDTA containing vial
2. Mix it properly and keep at room temperature
3. Overlay this blood sample on 2 ml Histopaque solution in 25-ml sterile centrifuge tube. Centrifuge the tube at 1500 rpm for 20 min
4. Two layers will be formed after centrifugation
5. Separate out the upper layer of Histopaque with the help of sterile pipette and collect the lymphocyte ring in 2 ml sterile eppendorf tube
6. Microfuge it for 1min at the bottom of the eppendorf tube lymphocytes sediment will be observed.
7. Resuspend the sediment in 2-ml fresh RPMI-C Media.
8. Prepare the serial dilutions of the drug of our interest or to be tested in the range of 1ug/ml – 500 ug/ml
9. Add 500 ul of the lymphocyte culture with the help of sterile pipette / tips and add the appropriate dilution of the drug to the respective culture well along with control without addition of any drug.
10. Incubate it in CO2 incubator at 37 degree Celsius (5% CO2)
11. After incubation do the P-24 ELISA test for Control and for Test
12. Interpret the results on the basis of difference in between the Control O.D and Test O.D and calculate the % Inhibition of the viral growth in test in comparison with Control.
13. Example: – O.D of the Control always ranges from 0.2-0.4 while the O.D of Test ranges in between 0.06-0.1 which indicates the inhibition of the virus multiplication.
Note:
This Test is having lots of significance over the other available tests in the Market as it gives the results within 24 Hrs very effective and economic too but requires skills of overlaying of the blood, preparation of Media, handling of the highly infectious viral lysates, result interpretation etc. Basic principle of the Test: We are giving the identical conditions for the growth of Virus in control as well as in Test. As we are treating the Test sample with the drug and after incubation the P-24 ELISA give us core protein formation during incubation comparison with control.
Significance of the Test:
Leading manufacturers of the ARV drugs in India designs the drug dosages after getting confirmation of this Test. It also plays key role in the optimization of the dosages for the patients.
Safety studies of the Support are:
- The Toxicological Studies, Storage Stability Studies and are being successfully made from the FDA Approved Lab.
- Purely herbal ingredients confirmed in HPTLC
- These medicines proved to be free from any inclusion of Steroids or Heavy Metals.
- These medicines are free from all toxic or spurious ingredients.
- The patient can test their Liver Function Test before & after Support.
The New upgraded Hoo-Imm Plus treatment had undergone the invitro anti-HIV colorimetric test in order to determine the percent inhibition of the drug against the (RT) Reverse Transcriptase and Integrase those are very important targets of HIV.
The kit used for the above test is as under:
1) HIV-1 reverse transcriptase Assay (Xpress Bio, USA)



The above test had proved that the New upgraded Hoo-Imm Plus course had recorded higher inhibition against HIV compared to the efavirenz which is one of the preferred NNRTI-based regimens used in HIV infected adults and adolescents and children.
Note: Any doctor, laboratory, hospital or government institution willing to confirm the above results can perform the above test at their facilities and we will provide them with free samples of the New upgraded Hoo-Imm Plus course, provided the shipping charges to their destination will be born by them.